What Causes Heel Pain To Appear
Overview
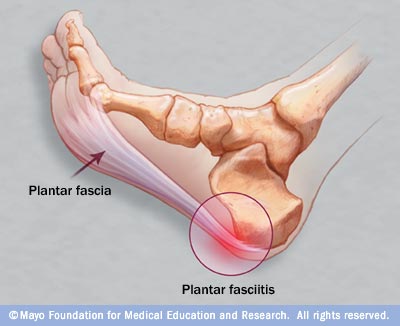
The plantar fascia is a strong, relatively inflexible, fibrous ligament band that runs through the bottom of the foot. That band helps to keep the complex arch system of the foot, absorb shock, plays a role in body balance and in the various phases of gait. The band transmits your weight across the bottom of the foot with each step you take. When the heel of the trailing leg starts to get off the ground, the band bears tension that is approximately twice the body weight. The tension on the band at this moment is even greater if the calf muscles are not flexible enough.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is caused by drastic or sudden increases in mileage, poor foot structure, and inappropriate running shoes, which can overload the plantar fascia, the connective tissue that runs from the heel to the base of the toes. The plantar fascia may look like a series of fat rubber bands, but it's made of collagen, a rigid protein that's not very stretchy. The stress of overuse, overpronation, or overused shoes can rip tiny tears in it, causing pain and inflammation, a.k.a. plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
People with this condition sometimes describe the feeling as a hot, sharp sensation in the heel. You usually notice the pain first thing in the morning when you stand. After walking for a period of time, the pain usually lessens or even disappears. However, sharp pain in the center of the heel may return after resting for a period of time and then resuming activity.
Diagnosis
A physical exam performed in the office along with the diagnostic studies as an x-ray. An MRI may also be required to rule out a stress fracture, or a tear of the plantar fascia. These are conditions that do not normally respond to common plantar fasciitis treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of plantar fasciitis begins with first-line strategies, which you can begin at home. Stretching exercises. Exercises that stretch out the calf muscles help ease pain and assist with recovery. Avoid going barefoot. When you walk without shoes, you put undue strain and stress on your plantar fascia. Ice. Putting an ice pack on your heel for 20 minutes several times a day helps reduce inflammation. Place a thin towel between the ice and your heel,do not apply ice directly to the skin. Limit activities. Cut down on extended physical activities to give your heel a rest. Shoe modifications. Wearing supportive shoes that have good arch support and a slightly raised heel reduces stress on the plantar fascia. Medications. Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation. If you still have pain after several weeks, see your foot and ankle surgeon, who may add one or more of these treatment approaches. Padding and strapping. Placing pads in the shoe softens the impact of walking. Strapping helps support the foot and reduce strain on the fascia. Orthotic devices. Custom orthotic devices that fit into your shoe help correct the underlying structural abnormalities causing the plantar fasciitis. Injection therapy. In some cases, corticosteroid injections are used to help reduce the inflammation and relieve pain. Removable walking cast. A removable walking cast may be used to keep your foot immobile for a few weeks to allow it to rest and heal. Night splint. Wearing a night splint allows you to maintain an extended stretch of the plantar fascia while sleeping. This may help reduce the morning pain experienced by some patients. Physical therapy. Exercises and other physical therapy measures may be used to help provide relief.

Surgical Treatment
The most dramatic therapy, used only in cases where pain is very severe, is surgery. The plantar fascia can be partially detached from the heel bone, but the arch of the foot is weakened and full function may be lost. Another surgery involves lengthening the calf muscle, a process called gastrocnemius recession. If you ignore the condition, you can develop chronic heel pain. This can change the way you walk and cause injury to your legs, knees, hips and back. Steroid injections and some other treatments can weaken the plantar fascia ligament and cause potential rupture of the ligament. Surgery carries the risks of bleeding, infection, and reactions to anesthesia. Plantar fascia detachment can also cause changes in your foot and nerve damage. Gastrocnemius resection can also cause nerve damage.
Stretching Exercises
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with this condition. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 2 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate and advanced exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head until you feel a stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon, plantar fascia or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Resistance Band Calf Strengthening. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot as demonstrated and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free.